|
|
| Menu location |
|---|
| Edit → Placement... |
| Workbenches |
| All |
| Default shortcut |
| None |
| Introduced in version |
| - |
| See also |
| Tasks Placement, Placement |
Descriere
Placement este modul în care FreeCAD specifică locația și atitudinea (orientarea) unui obiect în spațiu. Placement can be specified in multiple forms and manipulated via scripting, the Properties panel or the Edit → Placement... dialog.
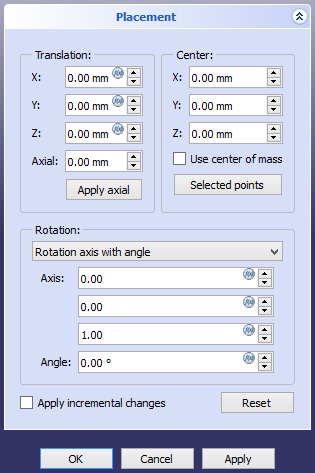
The Placement task panel
Utilizare
- Short description
- Select an object in the tree view.
- In the Edit menu, select Placements...
- Change the parameters for the translation or rotation, according to the desired action.
- Click OK or Apply
- For a full description see Tasks Placement and Placement
- Select a single object that has a DatePlacement property.
- Select the Edit →
Placement... option from the menu.
- Change one or more of the translation and rotation parameters.
- Do one of the following:
- Press the OK button to apply the changes and close the task panel.
- Press the Apply button to apply the changes, but keep the task panel open for further changes.
- Press Esc or the Cancel button to abort the operation. This will undo any changes that have not been applied.
The dialog can also be launched by clicking on the ellipsis button ... that appears in the Property editor when you click on the DatePlacement property.
Notes
- For more information about the placement parameters see the Placement page, and the Aeroplane tutorial.
- The rotation angle can be set in degrees in the GUI but is stored in radians internally so that angles usually have to be converted when used in scripts.
Scripting
See also: Autogenerated API documentation and FreeCAD Scripting Basics.
See the Python scripting tutorial.
A placement is internally defined by a matrix; in many cases it is simpler to represent it by means of two components, a Base point (vector), and a Rotation value. The Rotation itself has different representations; it can be entirely defined by the value of a "quaternion" (xi + yj + zk + w), but it can also be described by a rotation Axis (unit vector) and a rotation Angle (radians).
import FreeCAD as App
doc = App.newDocument()
obj = doc.addObject("Part::Cylinder", "Cylinder")
print(obj.Placement)
# Placement [Pos=(0,0,0), Yaw-Pitch-Roll=(0,0,0)]
print(obj.Placement.Base)
# Vector (0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
print(obj.Placement.Rotation)
# Rotation (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
print(obj.Placement.Rotation.Angle)
# 0.0
print(obj.Placement.Rotation.Axis)
# Vector (0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
print(obj.Placement.Rotation.Q)
# (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
Move the base point of the object, then rotate the object 45 degrees around the X axis.
The math module supplies a method radians() to easily convert degrees to radians and has to be imported at first.
import math
obj.Placement.Base = App.Vector(5, 3, 1)
obj.Placement.Rotation.Axis = App.Vector(1, 0, 0)
obj.Placement.Rotation.Angle = math.radians(45)
print(obj.Placement)
# Placement [Pos=(5,3,1), Yaw-Pitch-Roll=(0,0,45)]
print(obj.Placement.Rotation.Q)
# (0.3826834323650898, 0.0, 0.0, 0.9238795325112867)
print(obj.Placement.Matrix)
# Matrix ((1,0,0,5),(0,0.707107,-0.707107,3),(0,0.707107,0.707107,1),(0,0,0,1))
Această pagină este preluată de la https://wiki.freecad.org/Std_Placement